Flight Planning Calculator
GRYFN's Flight Planning Calculator allows users to calculate data characteristics from flight parameters. By inputting a flight altitude, speed, and spacing in the user-defined boxes, our calculator will display the corresponding ground sampling distance (GSD), overlap percentage, and other relevant characteristics. While the resulting values in the spreadsheet are color coded based on processing and product viability, the better resolution and overlap percentages, the better your products will be.
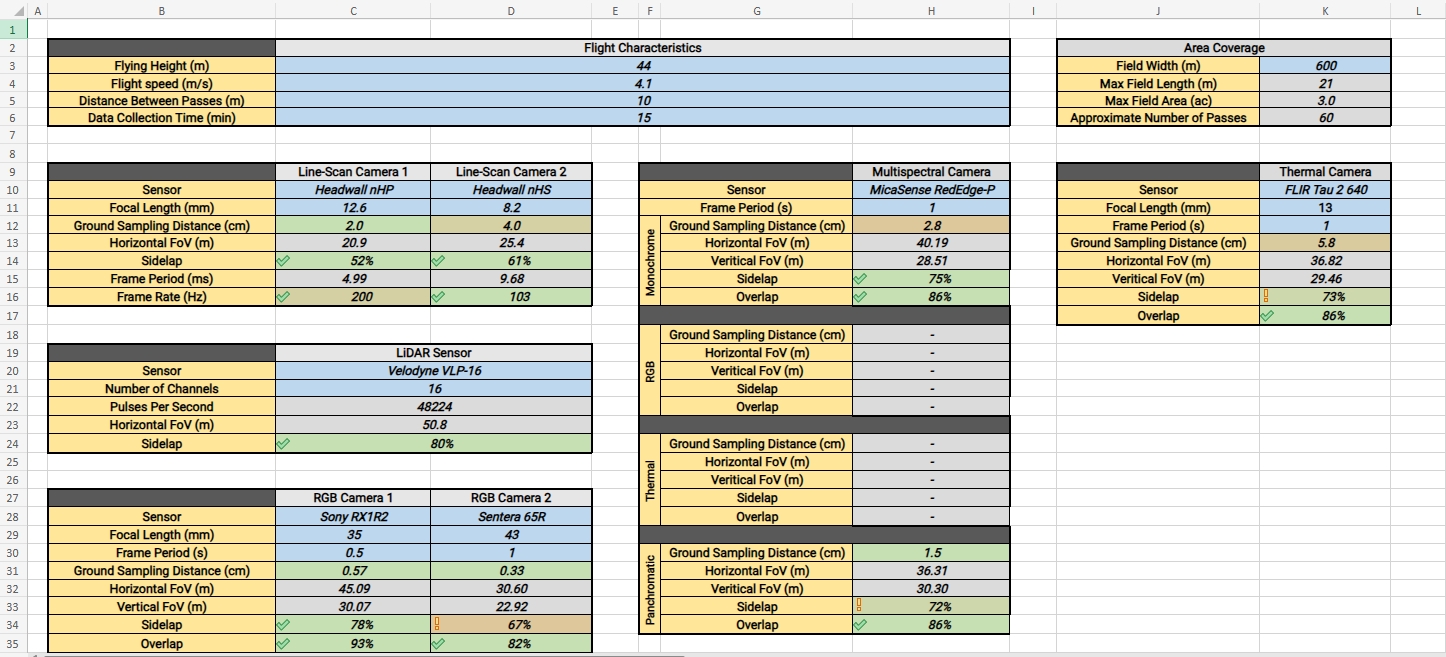
Standard Parameters
Line-Scan Hyperspectral
Line-scan hyperpsectral sensors typically do not require much overlap between adjacent flight lines (sidelap). Due to the nature of these sensors, data is layered on top of each other in the orthomosaic process. GRYFN recommends a minimum of 30% sidelap, this percentage should account for instability in aircraft roll.
LiDAR Sensors
LiDAR sensors can create point clouds with very little overlapping information between adjacent flight lines. Due to the restrictions from other sensors, LiDAR is typically well above acceptable ranges of sidelap. GRYFN recommends a minimum of 30% sidelap for LiDAR sensors.
Point density for LiDAR sensors will vary based on flight speed, distance to object, and sidelap percentage. To increase point density:
Fly slower
Shorten the distance between adjacent flight lines
Fly lower (proceed with caution)
RGB Frame Cameras
RGB frame cameras are typically the limiting factor around flight planning characteristics. They have the highest requirements for overlapping data and typically the lowest frame rate. GRYFN recommends an absolute minimum of 70% overlap and 70% sidelap in order to process an orthomosaic, although aiming for higher (80% for both) is likely to provide better feature matching results and therefore higher quality data products.
Last updated